- HOME
- HOME
- Technical Information
- How to select standard bellows
How to select standard bellows
About standard products
Standard products can be used under respective standard specifications.
If you adopt standard products as and when conditions permit, they can be conveniently used in terms of delivery time and price.
Discrete welded bellows
*Flick left or right to view.
Selection procedures1. Check specification conditions to see whether standard products can be used.
| Pressure conditions | (Internal) vacuum (External) atmospheric pressure |
|---|---|
| Temperature conditions | Ordinary temperature (baking temp. max. 250°C) |
| Operating conditions | Axial displacement only; at intervals of 10mm; up to maximum allowable displacement per block |
| Leak rate | 1×10-9 Pa・m3/s or less |
2. Select bellows material
*Flick left or right to view.
| Corrosion resistance |
Compact | Lifetime characteristics |
Softening of spring |
Magnetism | Material price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUS316L | ○ | ○ | ○ | ◎ | Non-magnetic | Low |
| AM350 equivalent | × | ◎ | ◎ | ○ | Magnetic | Higher than SUS |
3. Select lifetime.
10,000 repetitions or 100,000 repetitions or 1,000,000 repetitions
* If your specification life is not standard, move up one rank.
* For exceeding 1,000,000 repetitions, custom design is required.
4. Check the bellows size.
Interference check
・Check for interference with the shaft passing through the bellows.
A minimum clearance of 2mm is required on one side.
・Check for interference with the inner diameter of the externally interfering object outside the bellows.
A minimum clearance of 2mm is required on one side.
Interference check
・Check for interference with the shaft passing through the bellows.
A minimum clearance of 2mm is required on one side.
・Check for interference with the inner diameter of the externally interfering object outside the bellows.
A minimum clearance of 2mm is required on one side.
*Flick left or right to view.
| Model | Size | Model | Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22 | 8x22 | 109 | 79x109 |
| 30 | 17x30 | 120 | 90x120 |
| 36 | 22x36 | 150A | 100x150 |
| 51 | 36x51 | 150B | 120x150 |
| 70 | 50x70 | 210 | 160x210 |
| 90 | 60x90 | 270 | 206x270 |
| 94 | 70×94 | 320 | 260×320 |
5.Upon determination of material, lifetime, expansion/contraction, and size, select a compatible model from the table.
Maximum stroke
・Select so that the required stroke falls within the allowable stroke.
・If the allowable stroke is exceeded, “air buckling,” “horizontal sagging,” or “vertical contact” may occur.
End fitting
・When fittings are welded by the user or fittings are supplied by the user,
end fittings are Y-type (Y).
・When fittings are welded by us,
corrugated type (E) is selectable, which will enable a more compact design than Y-type (Y).
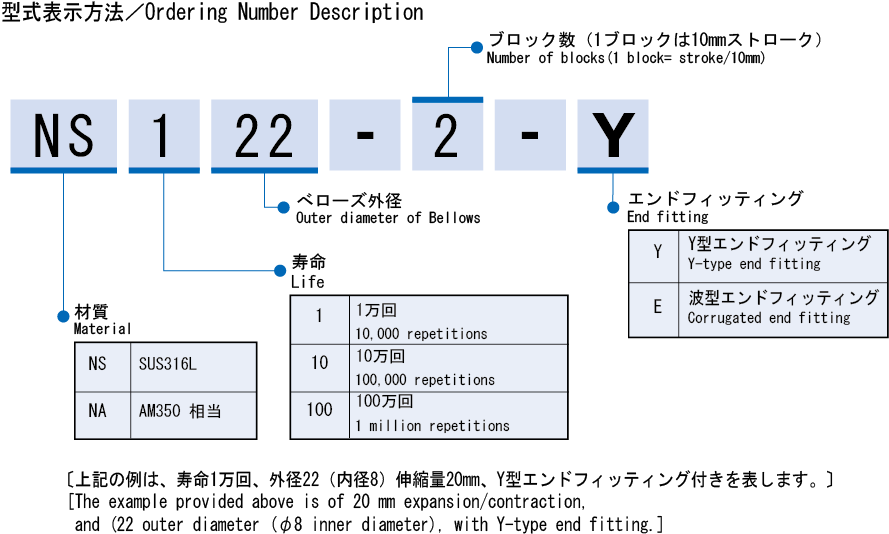
6. Check the operating range to see whether use within the target operating range is possible.
Note that the operating range of bellows should include end fitting lengths.
Unrestricted length = Unrestricted length (list) × (required stroke/10) + end fitting × 2
Maximum length = Maximum length (list) × (required stroke/10) + end fitting × 2
Minimum length = Minimum length (list) × (required stroke/10) + end fitting × 2
7.Check the spring constant in the axial direction.
Axial direction spring constant = Axial direction spring constant (list) / (required stroke/10)
・When fittings are welded by us,
corrugated type (E) is selectable, which will enable a more compact design than Y-type (Y).

6. Check the operating range to see whether use within the target operating range is possible.
Note that the operating range of bellows should include end fitting lengths.
Unrestricted length = Unrestricted length (list) × (required stroke/10) + end fitting × 2
Maximum length = Maximum length (list) × (required stroke/10) + end fitting × 2
Minimum length = Minimum length (list) × (required stroke/10) + end fitting × 2
7.Check the spring constant in the axial direction.
Axial direction spring constant = Axial direction spring constant (list) / (required stroke/10)
Flanged welded bellows, formed bellows, and flexible tubes
1. Check to see whether the flange shape you want to use is available.
2. Consider bellows type.
2. Consider bellows type.
*Flick left or right to view.
| Type | Expansion/contraction properties |
Airtightness | Spring properties |
Pressure resistance |
Bendability | Washability | Contamination | Mass producibility | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Welded | ◎ | ◎ | 軟 | ◎ | ◎ | △ | △ | ○ | ○ |
| Formed | ○ | ◎ | 硬 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ◎ | ◎ |
| Flexible | × | ◎ | × | × | ◎ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ◎ |
3. Check specification conditions to see whether standard products can be used.
4. Check the bellows size.
Interference check (excluding flexible tubes)
・Check for interference with the shaft passing through the bellows.
A minimum clearance of 2mm is required on one side.
・Check for interference with the inner diameter of the externally interfering object outside the bellows.
A minimum clearance of 2mm is required on one side.
5. If bellows specifications are met, select a compatible model from the table.
6. For different lengths of formed bellows, specify the lengths.
Glossary of bellows terms
Product Information List
Inquiry
For document requests and inquiries,
Please contact us using the email form below or by phone.