- HOME
- HOME
- Technical Information
- Bellows glossary
- Displacement types
Displacement types
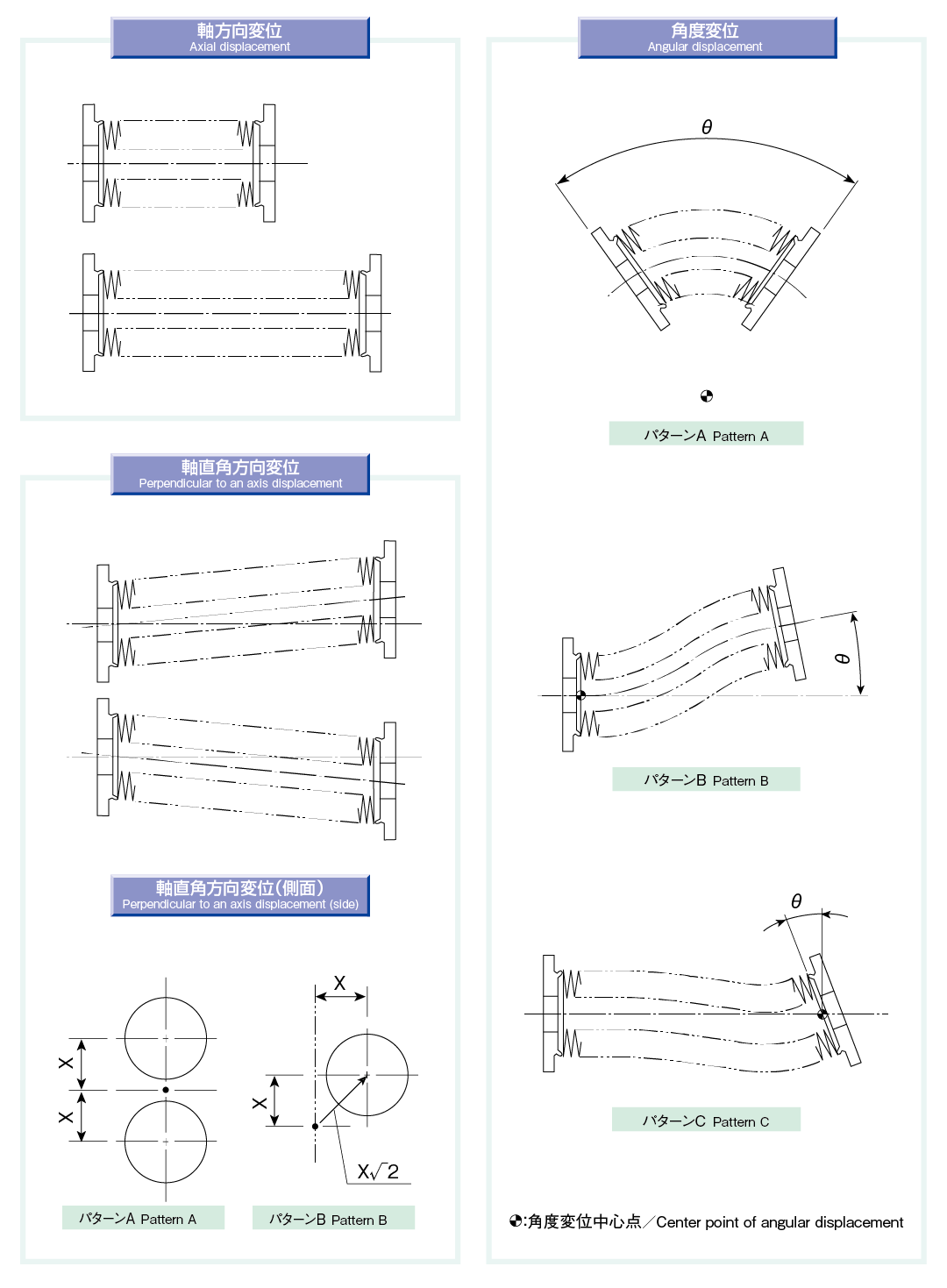
Bellows are expansion joints, which are used to absorb displacements. Types and forms of expansion/contraction are shown.
Displacement types
※左右にフリックしてご覧いただけます。
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Axial displacement | Basic displacement that changes only in the length direction of bellows |
| Perpendicular-to-an-axis displacement |
Displacement that changes parallel at one end as the length of bellows is constant * Assuming that the displacement directions are X direction and Y direction perpendicular to it, caution is required because effects on performance vary depending on whether displacements occur simultaneously in the X and Y directions(XY complex displacement: pattern B) or singly in the X or Y direction (XY single displacement: pattern A) |
| Angular displacement | Displacement that changes as the end-face angle of bellows differs * Caution is required because the load applied to the bellows differs according to the difference in the center position of angular displacement The load is the lightest when the center point of the bellows is the center of angular displacement |
| Single displacement | Axial, perpendicular-to-an-axis, or angular displacement that occurs by only one condition |
| Complex displacement | Axial, perpendicular-to-an-axis, or angular displacement that occurs by two or more conditions |
| Offset displacement | Displacement that occurs in an axial direction with a certain displacement in a perpendicular-to-an-axis direction |
Glossary of bellows terms
Product Information List
Inquiry
For document requests and inquiries,
Please contact us using the email form below or by phone.